
March 5, 2026

Over the past three years, InnoRenew CoE has collaborated with the Institute for the Protection of Cultural Heritage of Slovenia and the Slovenian National Building and Civil Engineering Institute on a national research project “Protection of bronze monuments in the changing environment”, financed by the Slovenian Research Agency (ARRS).
The aim of the project, concluded in June of this year, was to develop a holistic approach for the care of bronze cultural heritage objects. To support this, researchers developed IT tools and a set of environmental sensors capable of monitoring localized weather conditions in four bronze monuments around Slovenia.
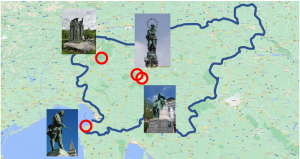
Set of environmental sensors installed at four bronze monuments around Slovenia. Image: Jakub Sandak
Their results indicate that the environment has an important influence on corrosion; for instance, in Piran, salt is a crucial factor, and sulfur plays a role in Ljubljana.
The Tartini monument in Piran is one of the bronze monuments included in the study. Researchers prepared and placed a plaque next to it with which they want to encourage people to share photographs of the monument on a dedicated webpage. On one hand, the collection of this data will serve researchers to make it easier and faster to detect the corrosion processes of bronze monuments, and on the other hand, more awareness of this topic will be created as people uploading their pictures to the webpage will gain access to a series of educational videos in Slovene, Italian and English.
Greater engagement of the public in the protection of cultural heritage objects was also one of the project’s goals. The plaque will be at Tartini square until February. Later researchers will review the received photographs, remove the inappropriate ones and publish the remaining as a publicly accessible database, available to interested researchers.

A plaque to encourage people to share the monuments photographs on the dedicated webpage. Image: Lea Primožič
More about the project can be found in the article Kako deljenje fotografij Tartinijevega spomenika prispeva k zaščiti kulturne dediščine? published by RTV Slovenia.
Everyone is invited to visit the Tartini monument, take a photo of it and upload the image to help researchers better protect bronze monuments of cultural heritage.